What are hypomineralized teeth?
What causes hypomineralized teeth?
Cause of disturbances in enamel formation:
- Hereditary factors: An element of genetics has been seen in hypomineralized teeth.
- Deficiencies: Vitamin deficiencies in the mother during pregnancy or in the child in the first two years of life can lead to hypomineralized teeth.
- Diseases: Some genetic and lifestyle diseases also affect the bone and teeth of the body.
- Nutritional problems: Low birth weight and subsequent malnutrition can also result in hypomineralized teeth.
- Premature birth: Children born prematurely are also at an increased risk for hypomineralized teeth.
- Infections: Severe infections in the mother that have the potential to cross the placental barrier or infections in children in infancy can lead to chalky teeth
- Trauma: Traumatic injury to teeth before their formation and eruption can disrupt tooth enamel's matrix building, causing hypomineralized teeth.
What are the symptoms of hypomineralized teeth in children?
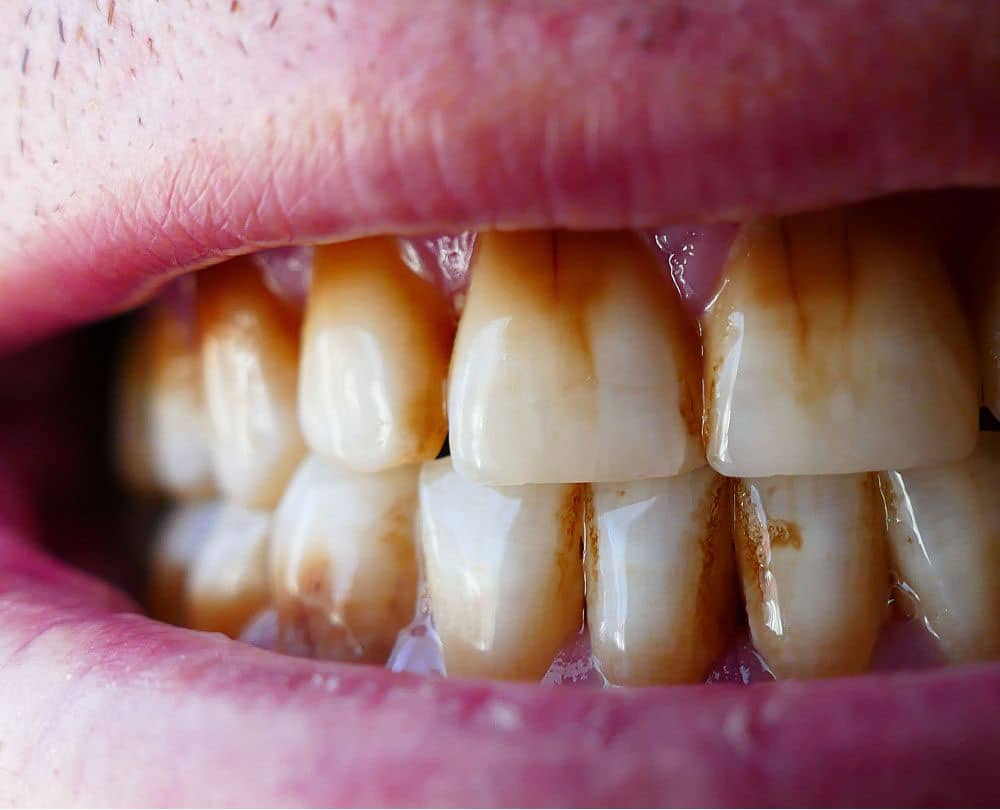
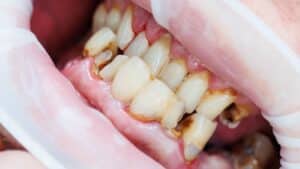
- Lesions: These are bumpy, discolored areas on the tooth surfaces, which can be chalky or cheesy white/yellow. There is a definite distinction between these areas and normal enamel.
- Atypical caries: If the teeth are hypomineralized, they start to decay soon as they erupt. The teeth with yellow and brown spots tend to decay faster as these color lesions show even lower mineral content of enamel, thus making it more porous.
- Hypersensitivity: Often, children complain of sensitivity in hypomineralized teeth when eating hot and cold foods. Some studies suggest that the easy movement of oral bacteria into the dentin due to weakened enamel can make teeth hypersensitive even while brushing teeth.
- Tooth breakdown and restoration problems: During restorative procedures, dental drilling and dental excavations can cause extensive tooth breakdown due to a weakened hypomineralized structure.
What are the long-term consequences of untreated hypomineralized teeth in children?
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit, the pediatric dentist of Pandit Clinic, Pune, wants parents to take hypomineralized teeth in children seriously. She recommends they visit a pediatric dentist as soon as they spot hypomineralized spots on teeth or even a single tooth, as the following problems may occur, jeopardizing the child’s dental health:
- Higher risk of tooth decay: Calcium and fluoride are essential to prevent caries. Hypomineralization causes dental decay to set in faster in the enamel.
- Difficulties in dental treatments: Dentists have a hard time working on hypomineralized teeth as they are difficult to anesthetize. This could be due to the inflammation of root canals due to the entry of microflora via a weakened enamel and dentin. This makes it problematic to perform dental procedures which require local anesthesia.
- Aesthetic issues: Chalky and bulky enamel patches on the front teeth can be an aesthetic concern, making the child self-conscious and affecting the quality of life.
Why is early intervention necessary for hypomineralized teeth?
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit asserts that early treatment for hypomineralized teeth can help to:
- Prevent further damage and progression: Treatment at the early stages can help to reduce further damage and progression of hypomineralized teeth. Early intervention can help to preserve a greater portion of the tooth structure, thus reducing the need for more extensive treatments like crowns, bridges, and other restoration in the future.
- Minimize pain and discomfort: Early treatment can help reduce the pain and discomfort associated with hypomineralized teeth by reducing hypersensitivity. It can even help in future dental treatments as anesthesia can be given more easily to teeth that have not been damaged too much.
- Reduce future risks of tooth decay: Early intervention and restoring the enamel can help to reduce the risk of tooth decay as hypomineralized teeth are more prone to decay.
What are some of the treatments available for hypomineralized teeth?
Depending on the stage and severity of the hypomineralization, the pediatric dentist may:
- Observe it and prescribe fluoridated toothpaste or fluoride varnish application to help with remineralization.
- Advise dental restorative procedures like dental sealants and pre-formed dental crowns to retain the remaining structure of the primary tooth until its shedding time.
If there is pulp exposure, the dentist may recommend removing the infected pulp and placing a crown.
The most ideal treatment plan will be advised by your dentist depending upon the severity of hypomineralization in every tooth and how it will affect the permanent dentition. The parents need to make an informed decision about which is best for their child.
What are the types of pulp therapy?
How can parents ensure that their child's dental health is maintained?
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit mentions that apart from clinical work, home care is equally vital. For example, brushing with fluoridated toothpaste and avoiding trigger foods for dental caries can help preserve your child’s hypomineralized primary teeth and prevent future problems. Here are some home care guidelines that should be followed:
- Parents should start brushing their child’s teeth as soon as they develop their first tooth.
- They should counsel children to brush twice daily once they reach the toddler phase.
- Parents should make sure that snacking between meals is limited, and food items such as chocolates, biscuits, and other sticky foods should be avoided.
- Parents should also make the children gargle their teeth after every meal or after eating anything, as hypomineralized teeth tend to develop caries faster.
- Parents should monitor their child’s teeth every four weeks to check for new cavities/pits or discoloration.
- Contact the pediatric dentist when your child reports trouble eating hot or cold foods or complains of pain.
In fact, parents should schedule a visit to a pediatric dentist every six months for their children, even if they have excellent dental health.
If you have any questions or concerns, please don’t hesitate to contact us at +918805980048 / +91-7888229284 or book an appointment with Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit.
Virtual Video Consultations
100% SAFE AND SECURE CALLS WITH ENCRYPTION. YOUR PRIVACY AND CONFIDENTIALITY IS GUARANTEED.
Start here, by making an appointment for a virtual consultation with our expert Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit (NEW PATIENTS ONLY).
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit is available for Virtual Video Consultations from Monday – Saturday between the hours of 11 am – 2pm and 4pm – 7pm.
If you are already our valued patient with questions or have an emergency please contact the clinic on +91 9822053446
Consult Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit
(Pediatric Dentist)
Virtual Video Consultation Fees Rs. 500
The Consultation Fees Must Be Paid Online by GOOGLE PAY BEFORE YOUR APPOINTMENT. See The Instructions On Appointment Confirmations
Your virtual video consultation includes:
- Discussion of problems that your child is facing like tooth pain, swelling or any other emergencies
- Dr. Pratibha will recommend a course of treatment or medications for your child.
Meet the Doctor
Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry Specialist
Dr. Pratibha is the Chief Dentist at Pandit Clinic. She is also a Consultant Pediatric Dentist at Kotbagi Hospital and KEM Hospital, Pune.
Dr. Pratibha has trained at the prestigious Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan, in advanced areas including Pediatric dental treatment under General Anesthesia and Intravenous sedation, Dental Rehabilitation of children with special health care needs, and Nasoalveolar molding and dental rehabilitation of cleft lip and cleft palate.
She’s the lifetime member of Student Clinician Association, American Dental Association (SCADA), USA.
Professional Affiliations and Skills
- Trained in Pediatric dental treatment under General Anesthesia and Intravenous sedation at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan
- Trained in Dental Rehabilitation of children with special health care needs at CGMH, Taiwan
- Trained in Nasoalveolar molding and dental rehabilitation of Cleft lip and Cleft Palate at craniofacial centre, CGMH, Taiwan
- Awarded Lifetime membership, SCADA (Student Clinician Association, American Dental Association), USA.
You Might Be Interested In

How Safe Is Local Anesthesia for Kids at the Dentist in Pune
A visit to the dentist can feel overwhelming for children—and, let’s admit it, sometimes even for their parents. But with the evolution of pediatric dentistry,
Panicked about Early Childhood Caries? Dr. Pratibha Has Your Back!
“Tiny teeth trembling, dental caries looming near, Dr. Pratibha’s got magic, banish all your fear!” Dental caries Imagine the joyous symphony of laughter echoing through